Hydroponic vs Aeroponic Gardens: How They Differ
Of the different gardening systems available, most readers ask about the difference between hydroponic vs aeroponic garden systems. These systems have gained popularity, and both offer innovative and efficient ways to grow plants without soil, but differ in their approaches and methodologies.
We will guide you through the nuances of hydroponic vs aeroponic gardening, exploring their advantages, disadvantages, and the key differences between them. By understanding these differences, you can make an informed decision about which system suits your gardening goals and preferences.
Contents Covered
- What is Hydroponic Gardening?
- Advantages and Disadvantages
- What is Aeroponic Gardening?
- Advantages and Disadvantages
- Comparison of Hydroponic vs Aeroponic
- Water and Nutrient Delivery
- Growth Medium
- Plant Health and Growth
- Maintenance and Cost
- Plant Health and Growth
- Maintenance and Cost
- Choosing the Right System: Hydroponic vs Aeroponic
- Considerations for Beginners
- Space Availability and Climate
- Plant Types
- Personal Preference and Experimentation
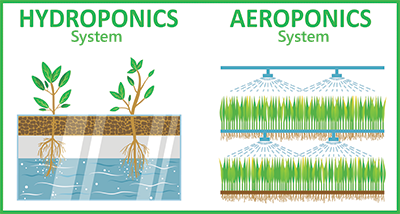
What is Hydroponic Gardening?
Hydroponic gardening is a method of growing plants without soil, where the plants receive essential nutrients directly from a nutrient-rich water solution. It involves the use of a growth medium to support the plants’ roots and deliver the nutrient solution. Hydroponic gardening offers several advantages, such as efficient water usage, controlled nutrient delivery, and the ability to grow plants in various environments. However, it also has drawbacks that should be considered.
Advantages
- Efficient water usage: Hydroponic systems recirculate water, resulting in less water waste compared to traditional soil-based gardening.
- Controlled nutrient delivery: The nutrient solution can be tailored to meet the specific needs of plants, promoting best growth and higher yields.
- Faster growth and higher yields: With proper care and management, plants in hydroponic systems tend to grow faster and produce more bountiful harvests.
- Year-round gardening: Hydroponics allows for year-round gardening, as the growing conditions can be controlled irrespective of external climate.
Disadvantages
- Initial setup costs: Hydroponic systems require an investment in equipment, such as pumps, timers, and nutrient solutions, which can be expensive.
- Technical knowledge required: Hydroponic gardening involves understanding and managing nutrient solutions, pH levels, and potential system malfunctions.
- Monitoring and maintenance: Regular monitoring of pH levels, nutrient levels, and system maintenance is necessary to ensure best plant health.
- Power dependency: Several hydroponic systems rely on electricity to run pumps and supply artificial lighting, resulting in increased energy consumption.
What is Aeroponic Gardening?
Aeroponic gardening takes the concept of hydroponic gardening a step further by delivering nutrients directly to the plant’s roots in the form of a fine mist or spray. In aeroponic systems, plants are suspended in the air or within a growing chamber, and their roots are misted at regular intervals with a nutrient-rich solution. This method allows for increased oxygenation of the roots and promotes faster growth and nutrient absorption.
- Enhanced nutrient absorption: The misting of nutrient solution supplies optimal nutrient uptake for plants, leading to accelerated growth and healthier plants.
- Increased oxygenation: The exposure of roots to air in aeroponic systems promotes oxygenation, which is vital for root health and overall plant vitality.
- Water conservation: Aeroponic systems use minimal amounts of water compared to traditional gardening methods, making them highly water efficient.
- Space efficiency: Aeroponic systems allow for vertical gardening and can maximize limited space, making them ideal for urban environments or small gardens.
Disadvantages
- Technical complexity: Aeroponic systems can be more complex to set up and maintain than traditional gardening methods, requiring a good understanding of misting cycles, nutrient concentrations, and pH levels.
- Vulnerability to power outages: As aeroponic systems heavily rely on pumps and misting mechanisms, power outages or equipment malfunctions can quickly affect plant health.
- Initial investment: Aeroponic systems require an initial investment in equipment and maintenance, which may deter a few gardeners – like Hydroponic systems.
- Regular monitoring: Monitoring and adjusting misting cycles, nutrient levels, and pH is crucial to ensure the system’s proper functioning.
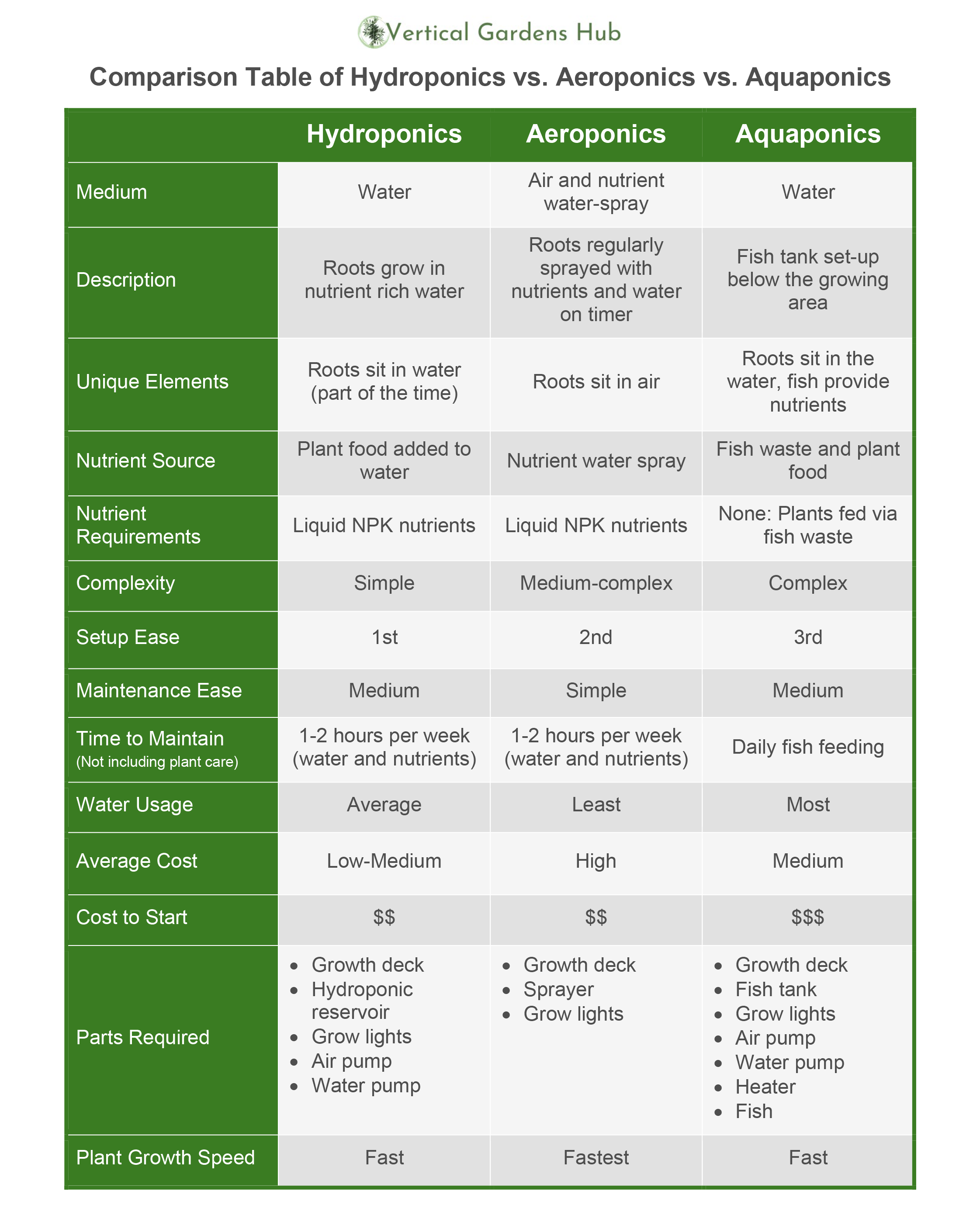
Comparison of Hydroponic vs Aeroponic Gardening
While both hydroponic and aeroponic gardening systems share the commonality of growing plants without soil, there are key differences between them.
Water and Nutrient Delivery
- Hydroponic gardening uses a growth medium, such as perlite, coconut coir, or rockwool, to support the plants’ roots and deliver the nutrient solution.
- Aeroponic gardening, on the other hand, delivers nutrients to the roots by misting them with a nutrient-rich solution, promoting enhanced nutrient absorption and oxygenation.
Growth Medium
- Hydroponic systems rely on a growth medium to support the plants’ roots and provide stability.
- Aeroponic systems do not require a growth medium as the plants’ roots suspend in the air and receive nutrients through misting.
Plant Health and Growth
- Both hydroponic and aeroponic gardening methods promote accelerated plant growth and higher yields compared to traditional soil-based gardening.
- Aeroponic gardening, with its increased oxygenation and nutrient absorption, can result in even faster growth and healthier plants.
Maintenance and Cost Difference: Hydroponic vs Aeroponic
- Hydroponic systems require regular monitoring of nutrient levels, pH, and system maintenance, which can involve additional costs and technical knowledge.
- Aeroponic systems, although more complex to set up and maintain, offer water and energy efficiency and can be suitable for space-limited environments.
Choosing the Right System: Hydroponic vs Aeroponic
When deciding between these gardening systems, there are factors to consider for the best fit for your gardening goals.
Considerations for Beginners
- Hydroponic systems are beginner-friendly, as they are easier to set up and maintain.
- Aeroponic systems are more suitable for experienced gardeners or those willing to invest time in learning and managing the system intricacies.
Space Availability and Climate:
- Hydroponic systems can be adapted to various spaces, including indoor and outdoor settings.
- Aeroponic systems, with their vertical gardening capabilities, are ideal for maximizing limited space and can be suitable for urban environments.
Plant Types:
- Consider the types of plants you wish to grow and their requirements in terms of light, space, and nutrient needs.
- Research which system aligns best with the plants you intend to cultivate and the desired outcomes.
Personal Preference and Experimentation:
- The choice between hydroponic and aeroponic systems depends on personal preference, and willingness to invest in setup and maintenance.
Final Thoughts
Hydroponic vs aeroponic gardening systems offer unique and efficient ways to grow plants without soil. While hydroponic systems rely on a growth medium and a nutrient-rich water solution, aeroponic systems deliver nutrients through misting, promoting enhanced nutrient absorption and oxygenation. Both systems have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between them depends on factors such as experience level, space availability, plant types, and personal preference. By understanding the differences between hydroponic and aeroponic gardening, you can select the system that aligns best with your gardening goals and embark on a rewarding journey of soilless cultivation.
FAQs:
Q: What are the main differences between hydroponic vs aeroponic gardening?
A: The main difference lies in the way water and nutrients are delivered to the plants. In hydroponic gardening, plants receive nutrients through a water solution delivered via a growth medium. In aeroponic gardening, plants are misted with a nutrient-rich solution, promoting enhanced nutrient absorption and oxygenation.
Q: Which system is more beginner-friendly, hydroponic or aeroponic gardening?
A: Hydroponic gardening is considered more beginner-friendly, as it is easier to set up and maintain. However, with proper research and learning, beginners can also succeed in aeroponic gardening.
Q: Can I grow a wider range of plants in hydroponic or aeroponic systems?
A: Both hydroponic and aeroponic systems can accommodate a wide range of plants. The choice depends on the specific needs and preferences of the plants you intend to grow.
Q: Do hydroponic and aeroponic systems require much maintenance?
A: Both systems require regular monitoring of nutrient levels, pH, and system maintenance. However, aeroponic systems may require more technical knowledge and attention due to the misting mechanism.
Q: Can hydroponic and aeroponic systems cbe used in both indoor and outdoor environments?
A: Yes, both systems can be adapted to various environments. Hydroponic systems are for indoors and outdoors, while aeroponic systems are used in limited space or urban settings.