Aquaponic Gardening: A Symbiotic Relationship
Aquaponic gardening is a fascinating and sustainable approach that combines aquaculture and hydroponics to create a thriving ecosystem of growing plants and cultivating fish in a symbiotic relationship. In this article, we’ll delve into how this system works, its advantages, challenges and how you can set up your own DIY aquaponic system.
Contents Covered
- How Aquaponic Gardening Works
- The Advantage of Aquaponic Gardening
- Environmental Benefits of Aquaponic Gardening
- Creating a DIY Aquaponic System
- Choosing Fish and Plants for Your Aquaponic Garden
- Maintaining Your Aquaponic Garden
- Harvesting and Utilizing Your Aquaponic Produce
- The Educational Value of Aquaponic Gardening
- Economic Viability and Food Security
- Challenges and Troubleshooting in Aquaponic Gardening
- Future Potential and Innovations
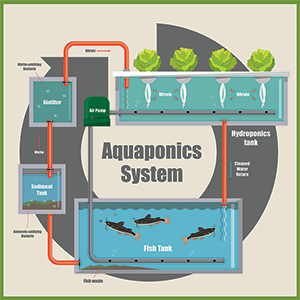
How Aquaponic Gardening Works
Aquaponic gardening is a closed-loop system that mimics a natural ecosystem, combining aquaculture (fish farming) and hydroponics (soilless plant cultivation). The process begins with fish living in a tank or pond, where they produce waste rich in ammonia. Instead of being a problem, this waste becomes a valuable resource in the aquaponic system.
The waste-filled water from the fish tank is pumped to the hydroponic grow beds, where plants are cultivated. Beneficial bacteria convert the toxic ammonia into nitrates, which serve as essential nutrients for the plants. The plants then absorb these nutrients, effectively purifying the water, which is subsequently returned to the fish tank. This continuous cycle creates a harmonious environment where both fish and plants thrive, benefiting each other in a mutually beneficial relationship.
The Advantages of Aquaponic Gardening
Efficient Use of Resources
One of the significant advantages of aquaponic gardening is its exceptional resource efficiency. Compared to traditional soil-based gardening, aquaponics uses up to 90% less water. The water recirculation system minimizes water waste, making it an ideal option for regions with water scarcity or for gardeners seeking to reduce their water consumption.
Additionally, aquaponics eliminates the need for chemical fertilizers, as fish waste provides a natural and nutrient-rich source for the plants. By avoiding synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, aquaponic gardening promotes healthier produce, free from harmful chemicals.
Benefits for Plant Growth and Fish Cultivation
Aquaponic gardening creates an ideal environment for plant growth. The continuous supply of nutrients from fish waste ensures that plants receive all the essential elements they need for robust development. This nutrient-rich water fosters faster growth and higher yields, making aquaponic gardens highly productive.
Moreover, the fish in the system benefit from the hydroponic grow beds acting as a biofilter. The plants’ roots naturally filter and purify the water, creating a clean and oxygenated environment for the fish to thrive.
Also Read:
- Vertical Hydroponic Gardening: How, Why and Types
- Hydroponics vs Aeroponic Gardens: How they differ
- Building an Aquaponic Gardening System: Step by Step Guide
- Aeroponic Gardening for Beginners: Understanding the Basics
Environmental Benefits of Aquaponic Gardening
Reduced Water Wastage and Conservation of Resources
Traditional soil-based gardening often leads to water runoff and wastage. Aquaponics, on the other hand, uses a closed-loop system that re-circulates water efficiently. This significantly reduces water consumption and wastage, making aquaponic gardening a sustainable water-saving practice.
Efficient water use in aquaponic systems contributes to water conservation efforts, especially in areas where water scarcity is a pressing concern. By adopting aquaponic gardening, we can contribute to the conservation of this precious resource.
Contribution to Biodiversity and Ecosystem Health
Aquaponic gardening promotes biodiversity by creating a habitat that supports various forms of life. The fish, plants, and beneficial bacteria work together in a harmonious ecosystem. This biodiversity extends to microorganisms and beneficial insects, which contribute to the overall health of the system.
As the aquaponic garden flourishes, it attracts pollinators, such as bees and butterflies, which further enrich biodiversity. By supporting a diverse range of species, aquaponic gardening contributes to a healthier and more resilient ecosystem.
Lower Carbon Footprint and Impact on Climate Change
Traditional agriculture often involves transportation and distribution processes that contribute to carbon emissions. In contrast, aquaponic gardening, especially when practiced locally, reduces the carbon footprint associated with food production.
Additionally, the closed-loop system of aquaponics prevents nutrient runoff into bodies of water, reducing the risk of harmful algal blooms and water pollution. By choosing aquaponic gardening, we can actively play a part in mitigating the impact of agriculture on climate change.
Creating a DIY Aquaponic System
If you’re eager to embark on the aquaponic gardening journey, creating your own DIY system is a rewarding and achievable project. While large-scale commercial systems exist, starting with a smaller system is ideal for beginners.
Remember, starting small allows you to learn and adjust before scaling up to a larger aquaponic system.
Choosing Fish and Plants for Your Aquaponic Garden
Selecting the right fish and plants is essential for a successful aquaponic garden. Factors to consider include your location, climate, available space, and personal preferences.
Suitable Fish Species for Aquaponic Gardening
- Tilapia: Tilapia is a popular choice for aquaponics due to its adaptability and rapid growth. They thrive in warm water conditions and can tolerate varying water quality.
- Catfish: Catfish are hardy and well-suited to aquaponic systems. They prefer slightly cooler water temperatures and are a great option for those living in cooler climates.
- Goldfish: Goldfish are a beginner-friendly option and add a decorative element to your aquaponic garden. They prefer milder temperatures and can withstand various water conditions.
Edible and Ornamental Plants That Thrive in Aquaponic Gardening
- Lettuce and Leafy Greens: Lettuce, kale, spinach, and other leafy greens grow exceptionally well in aquaponic systems. They have relatively short growth cycles and are highly nutritious.
- Herbs: Basil, mint, parsley, and other herbs thrive in aquaponic grow beds. Their aromatic presence can also deter certain pests.
- Tomatoes: Tomatoes are a popular choice for aquaponic gardeners, thanks to their high productivity and delicious fruits.
- Cucumbers and Peppers: These vining plants do well in aquaponic systems and produce an abundant harvest.
Remember to research the specific requirements of each fish and plant species to ensure a successful and thriving aquaponic garden.
Maintaining Your Aquaponic Garden
Maintaining an aquaponic system involves regular monitoring and attention to the needs of both the fish and plants. Here are some essential maintenance tasks to keep your aquaponic garden in top shape:
Monitoring Water Quality and pH Levels
Regularly check the water quality parameters, including ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels. A balanced nitrogen cycle is vital for the health of both fish and plants. Keeping the pH levels within the optimal range is crucial for nutrient uptake by the plants.
Proper Feeding and Care of Fish and Plants
Feed your fish a balanced diet appropriate for their species. Overfeeding can lead to excess waste, affecting water quality. Ensure your plants receive sufficient nutrients and adjust their feeding as needed to maintain growth.
Preventing and Managing Common Issues
Watch out for any signs of stress or diseases in your fish and promptly address any issues. Keep an eye out for nutrient deficiencies or pest infestations in your plants and take appropriate measures to resolve them.
Remember that aquaponic gardening requires a balance between the fish and plant components, so any issues affecting one can have repercussions on the other.
Harvesting and Utilizing Your Aquaponic Produce
One of the joys of aquaponic gardening is the ability to harvest fresh, homegrown produce right from your indoor or outdoor garden. Here are some tips for a continuous harvest and creative ways to enjoy your bounty:
Tips for a Continuous Harvest of Fresh Produce
Harvest leafy greens, herbs, and smaller fruits like tomatoes and cucumbers regularly to encourage continuous growth. With proper pruning and care, plants can yield harvests throughout the growing season.
Creative Recipes and Ways to Enjoy Your Homegrown Fish and Vegetables
Incorporate your homegrown produce into a variety of delicious and nutritious dishes. Create fresh salads with a mix of greens, use herbs to season your meals, and savor the flavors of ripe tomatoes and peppers in various recipes.
Don’t forget to share the fruits of your labor with friends and family, showcasing the joys of aquaponic gardening and sustainable food production.
The Educational Value of Aquaponic Gardening
Aquaponic gardening presents an excellent opportunity for education, both in schools and learning centers and for home-based learning experiences.
Incorporating Aquaponics in Schools and Learning Centers
Aquaponic systems in educational settings provide hands-on learning opportunities for students. They can learn about the principles of aquaponics, the nitrogen cycle, and the symbiotic relationship between fish and plants.
By participating in the care and maintenance of an aquaponic system, students gain a deeper understanding of sustainable food production and the importance of preserving natural resources.
Teaching Sustainability and Hands-on Experience
Aquaponic gardening aligns with the principles of sustainability, teaching students about responsible resource management, environmental stewardship, and the importance of growing food locally.
Through hands-on experience, students can connect with nature, cultivate a sense of responsibility towards the environment, and develop valuable life skills.
Economic Viability and Food Security
Aquaponic gardening has the potential to offer economic opportunities and contribute to food security.
Aquaponics as a Potential Income Source
Aquaponic produce, especially fresh fish and premium vegetables, can be sold in local markets or to restaurants, providing a potential income source for aquaponic gardeners.
Role in Promoting Local Food Production and Food Security
Aquaponic gardening supports local food production, reducing the need for long-distance transportation of produce. This, in turn, contributes to food security by providing access to fresh and nutritious food within the community.
Challenges and Troubleshooting in Aquaponic Gardening
While aquaponic gardening offers numerous benefits, it also comes with its challenges.
Maintaining water quality and nutrient balance is a critical aspect. Be vigilant about any changes in water parameters and take corrective actions promptly.
Dealing with potential pest infestations or diseases in plants requires prompt intervention to prevent their spread throughout the system.
Future Potential and Innovations
The future of aquaponic gardening holds exciting innovations. Advancements in aquaponics research and technology continue to improve system efficiency and productivity. And can also play a vital role in urban agriculture, contributing to green spaces, local food production, and sustainable living.
Aquaponic gardening is a remarkable and sustainable way to cultivate fresh produce while enjoying the companionship of fish. Its resource efficiency, environmental benefits, and potential for economic viability make it an attractive choice for sustainable gardening enthusiasts.
Conclusion
By understanding the symbiotic relationship between fish and plants, choosing suitable species, and maintaining water quality, you can create a thriving aquaponic system. Whether you’re a gardening enthusiast, an educator, or simply someone interested in sustainable food production, aquaponic gardening offers a rewarding and enriching experience.

FAQs
Q: What is aquaponic gardening?
Aquaponic gardening is a sustainable and innovative method that combines aquaculture (fish farming) and hydroponics (soilless plant cultivation) in a closed-loop system. In this symbiotic relationship, fish waste provides nutrients for plants, and the plants filter and purify the water for the fish.
Q: How does aquaponic gardening work?
Aquaponic gardening works by using fish waste as a natural fertilizer for plants. The fish excrete ammonia, which beneficial bacteria convert into nitrates. These nitrates serve as essential nutrients for the plants, which absorb them from the water. As the plants take up the nutrients, they help clean the water, which is then recirculated back to the fish tank.
Q: What are the advantages of aquaponic gardening?
Aquaponic gardening offers several advantages. It uses up to 90% less water than traditional gardening, conserving this valuable resource. It eliminates the need for chemical fertilizers, promoting healthier and organic produce. The system’s closed-loop nature reduces water wastage and carbon emissions, making it environmentally friendly. Also, it allows for year-round cultivation and maximizes space utilization.
Q: Can anyone do aquaponic gardening, or is it complex?
Aquaponic gardening is accessible to both beginners and experienced gardeners. While it involves some understanding of fish and plant care, many resources, guides, and community support are available to help novices get started. Starting with a small-scale DIY system is a great way to learn and gain confidence before scaling up.
Q: What types of fish and plants can I use in my aquaponic garden?
The choice of fish and plants depends on your location, climate, and personal preferences. For beginners, hardy fish species like tilapia, catfish, or goldfish are recommended. Leafy greens, herbs, tomatoes, cucumbers, and peppers are popular choices for plants. Research the specific needs of each species to ensure they thrive in your aquaponic system.